What Is Embedded Business Intelligence (2025 Guide)
What is embedded business intelligence? How should you start? Check out this express guide!
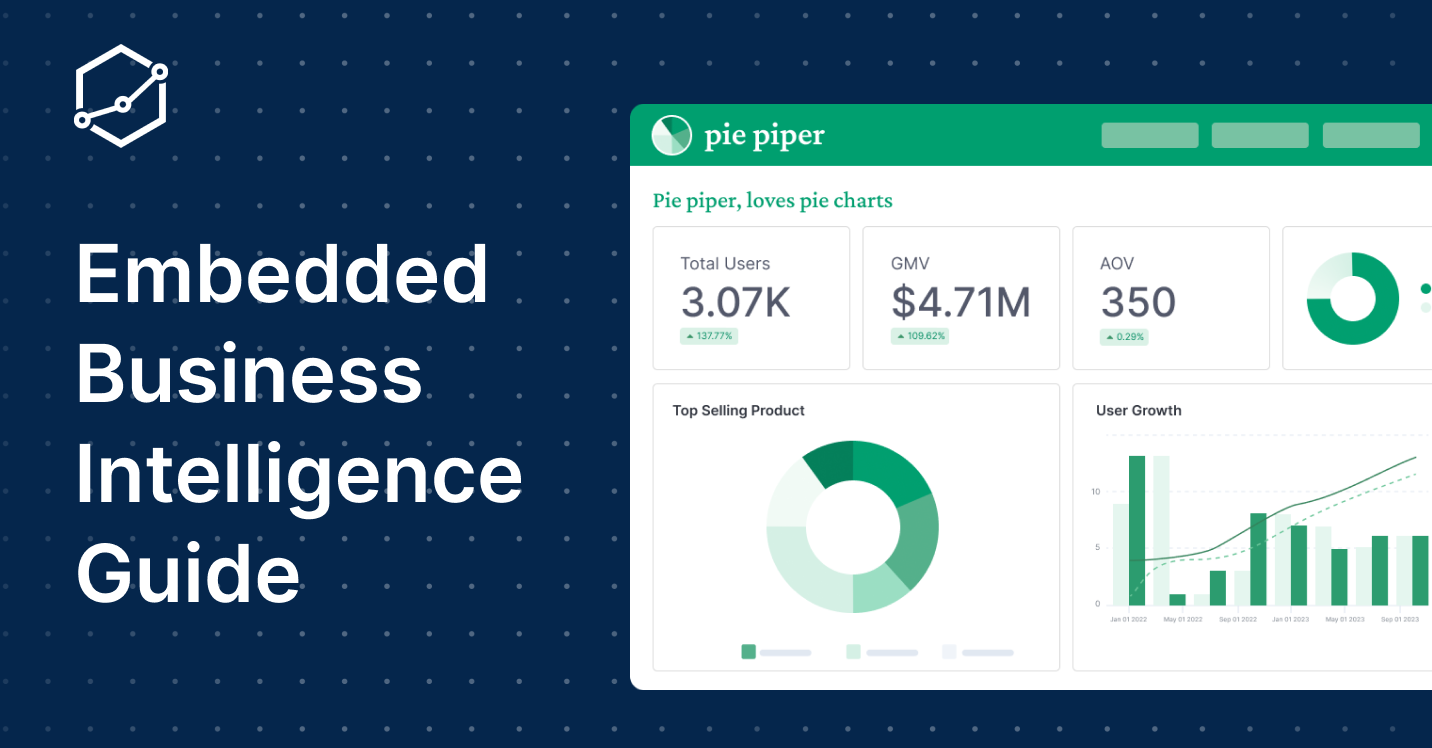
What Is Embedded Business Intelligence (BI)?
Embedded Business Intelligence (Embedded BI) is exactly what it sounds like—integrating BI capabilities directly into your existing applications. Think of it as embedding a data analyst right into your business software, delivering insights without the need to switch between platforms. This makes data-driven decisions a natural part of your workflow.
On a more technical note, Embedded Business Intelligence (Embedded BI), or embedded analytics, is described as the integration of analytics—such as visualizations, dashboards, reports, and even predictive analytics or artificial intelligence—directly into everyday business applications. This allows users to access and interact with data insights within the context of their daily workflows, rather than needing to switch between different applications or tools.
Here's an example of how embedded dashboard works.
Benefits of Embedded Business Intelligence
For SaaS product engineers and builders, adding embedded analytics to your product offers a range of valuable benefits:
- Enhanced Product Value: Integrating Embedded BI into your apps can significantly sharpen your product's value proposition. By delivering real-time insights directly within the application, you offer better the user experience and increase the perceived value of your product.
- Competitive Differentiation
In a crowded market, offering embedded analytics can set your product apart from the competition. It’s not just a feature—it’s a strategic advantage that appeals to businesses looking to consolidate tools and streamline operations. - Increased User Engagement: With embedded analytics, users spend more time within your application, leading to higher engagement rates. This increased interaction can improve user retention and create opportunities for upselling and cross-selling additional features or services.
- Scalability and Revenue Growth: Embedded BI allows you to reach a broader audience, including non-technical users, without requiring them to switch platforms. This expands your market appeal and can drive adoption, leading to growth and increased revenue.
- Simplified Data Management: By integrating analytics within your application, you reduce the need for users to export data to third-party tools. This keeps users within your ecosystem, simplifies data management, and enhances security.
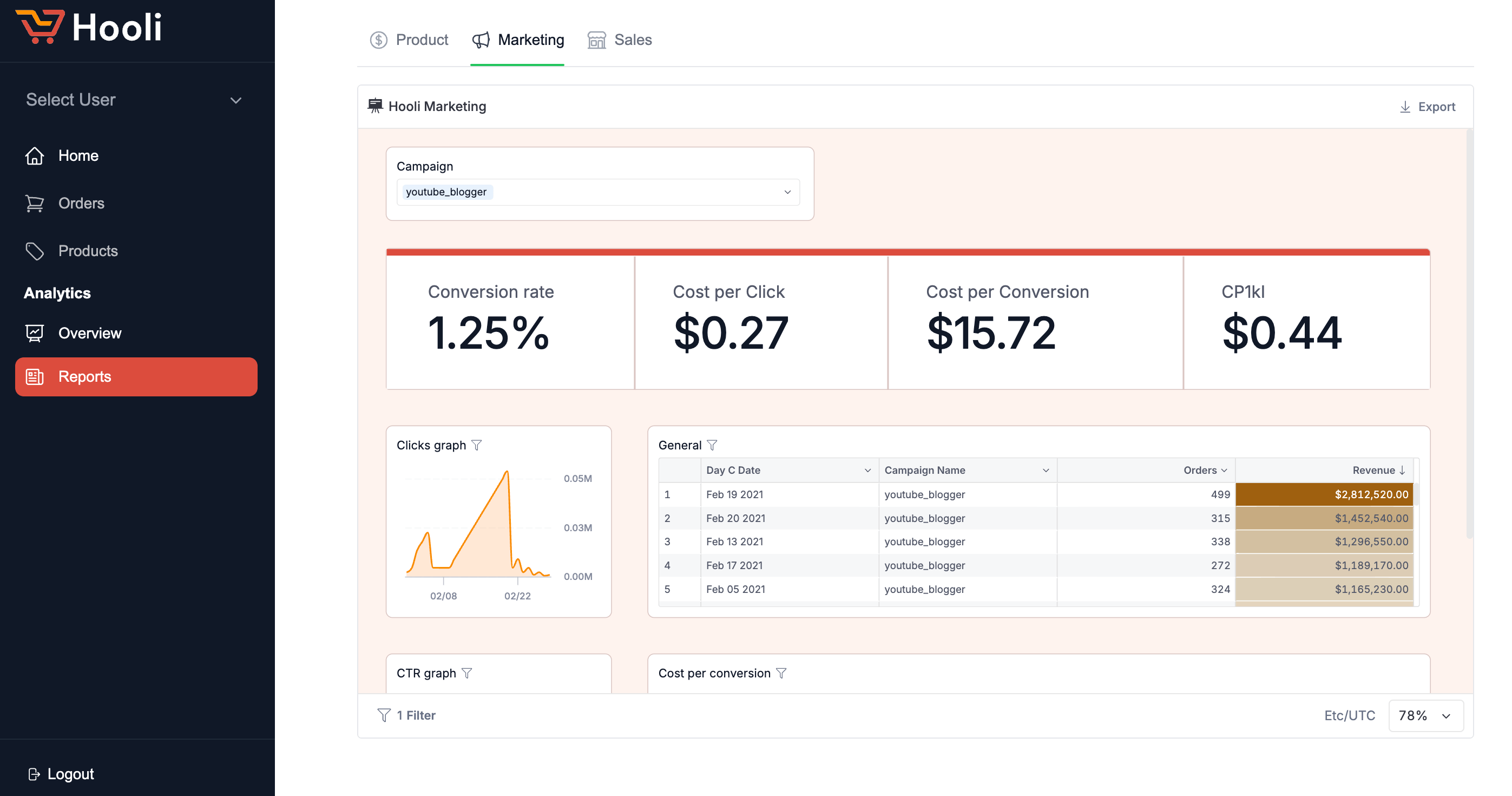
For your product users, having embedded analytics offers productivity and insightful benefits:
- Real-Time Data Insights Within Workflows: Users can access data-driven insights directly within their workflows, eliminating the need to switch between tools. This integration enables faster, more informed decision-making.
- Improved User Experience: EmbeddeD BI implifies the analytics experience by integrating it into tools users already know. This reduces the learning curve, making it easier for users to leverage data in their everyday tasks, leading to better outcomes and higher satisfaction.
- Self-Service Data Exploration: With easy access to real-time analytics, users can explore data and draw insights on their own. This empowerment leads to more strategic actions, helping users achieve their goals more effectively, whether in sales, operations, or customer service.
Core Capabilities of Embedded BI Tools
When implementing Embedded Business Intelligence, success isn’t just about plugging in some dashboards or data visualizations into your existing apps. It’s about creating a seamless, integrated experience that truly enhances how your team makes decisions.
Let’s break down the key capabilities and features you need to consider when designing your Embedded BI setup.
1. Integration Capabilities
Integration is the backbone of embedded analytics. The platform must blend seamlessly into existing software, whether it's an ERP, CRM, or a customer-facing application. The most common methods of integration include:
The most common methods of integration include:
- IFrames: This is the most basic form of embedding, allowing users to copy and paste HTML code into their applications for simple dashboards and visualizations(best-embedded-analytics…).
- SDKs and APIs: For more advanced integrations, developers rely on SDKs (Software Development Kits) and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to fully customize and embed analytics. This method allows for deeper integration, giving businesses the ability to tailor analytics to their specific needs(reveal-embedded-BI-feat…). For example, SDKs for JavaScript or React allow dynamic visualizations to fit perfectly into user workflows without requiring external tools(best-embedded-analytics…).
- Web Components: These offer a more modern approach to embedding, allowing analytics to be embedded directly into web applications using HTML tags. This method ensures flexibility while maintaining a clean, native integration experience(best-embedded-analytics…).
2. Self-Service Analytics
One of the standout features of Embedded BI is its user-friendly interface, making analytics accessible to everyone—not just the data pros. With self-service capabilities, users can create their own reports, dashboards, and visualizations without leaning on IT, driving higher engagement and satisfaction.
If your Embedded BI solution requires extensive training or feels like an added chore, adoption rates will plummet. Users should feel that the analytics enhance their workflow rather than disrupt it. Usability ties directly into the broader business impact—if the tool isn’t being used, it’s not delivering value.
Key self-service analytics features for embedded analytics:
- Non-technical users can independently create dashboards and reports with drag-and-drop interfaces.
- Drill-down and ad-hoc reporting for deeper data exploration
3. Customizable Dashboards and Reporting Features
Customization is a must-have with Embedded BI.
You should be able to tailor dashboards and reports to meet the specific needs of different teams or individual users. This means everyone gets the insights that matter most to them. Plus, the look and feel of these dashboards can be adjusted to match your product’s branding, ensuring a cohesive user experience.
Beyond basic customization,s some embedded BI tools provide advanced theming options, including light and dark modes, custom actions on visualizations, and the ability to override default events via APIs. This enables businesses to create a fully branded and personalized analytics experience that aligns with their product’s user interface.
Key customization features include:
- Full control over the appearance of dashboards and reports, matching the brand's look and feel through white-labeling.
- Custom buttons, filters, and drill-down capabilities to enhance interactivity.
- Theming options (light/dark modes) for user preference and consistency.
For example, here's a short demo of customized themeing in Holistics Embedded.
4. Real-Time Data & Alerts
Embedded BI tools are built to handle real-time data processing, meaning users get up-to-the-minute insights. This is critical for making timely decisions, especially in fast-paced environments where conditions can change quickly.
Additionally, you can set up alerts to notify users when certain thresholds are met or when significant changes occur, ensuring they never miss critical updates.
Key data alert features include:
- Email and Slack scheduling
- Anomaly Detection and Threshold-based data alerts
5. Multi-Tenancy
For SaaS providers, multi-tenant support is a must-have.
Embedded BI tools can manage data access across different clients or departments while maintaining security and privacy. Each tenant can have its own customized analytics environment, tailored to their specific needs, all while running on the same infrastructure.
6. SDK Availability & Developer Experience
Modern Embedded BI tools offer comprehensive SDKs (Software Development Kits) for both client-side and server-side, tailored for modern programming languages like C#, JavaScript, or TypeScript. This feature allows for deeper customization and control during deployment, making the integration process smoother for developers.
7. Strong Governance
Many modern embedded BI tools also offer strong governance capabilities by bringing DevOps best practices into analytics workflow. Developers can govern dashboards with Git Version control, perform code reviews of dashboard changes before publishing,and know who changes what and when.
How to Choose an Embedded BI Tool
Choosing the right Embedded Business Intelligence (BI) tool isn’t just about ticking off features on a list. It’s about finding the perfect fit for your business needs, ensuring that it integrates seamlessly with your existing systems, and, most importantly, delivering value to your users. Let’s break down the key factors you should consider.
1. Understand Your Needs: First things first—know what you’re looking for. Do your customers just want to view data and interact with it, or do they want the ability to create their own dashboards? Define your goals clearly. This clarity will guide your choice of tools.
2. Evaluate Integration Capabilities: One of the primary benefits of Embedded BI is the ability to integrate analytics directly into the applications your team already uses. Therefore, it’s essential to choose a tool that can easily connect to your existing data sources, whether they are on-premise databases, cloud storage, or third-party applications. Look for a tool that supports a wide range of data connectors and APIs, ensuring that it can integrate with your current systems without extensive customization or additional development work.
3. Consider Self-Service Capabilities: How important is it for your users to build and interpret their own dashboards? If empowering users with self-service BI is a priority, you’ll want a tool that’s easy to use, even for beginners. Some tools, like Tableau, can be complex for newcomers.
Consider tools that provide drag-and-drop functionality, customizable dashboards, and intuitive navigation. Additionally, the tool should offer a seamless user experience that aligns with the design and branding of your existing applications, ensuring a consistent look and feel.
3. Evaluate Time to Market: How quickly can you get up and running? Tools like Tableau and PowerBI are powerful, but they’re notorious for lengthy setup times. If you’re looking to get your embedded dashboards live quickly, you’ll need a tool that’s not only easy to use but also fast to deploy.
5. Assess Security & Compliance: Your end-users are concerned about the safety of their data, and so should you be. Make sure your BI tool complies with key regulations like GDPR and SOC-2. Look for features like row-level security, role-based access control, and support for multi-tenant analytics. This is especially crucial if you’re in a highly regulated industry like healthcare, where data breaches can have serious consequences.
6. Check Scalability and Performance: As your business grows, so will your data and the number of users accessing your BI tool. Choose a solution that can scale with you, both in terms of data volume, and user concurrency - without breaking the bank.
Look for solutions that offer cloud-based deployment options, which can provide elastic scalability to handle increased data loads and user concurrency. Additionally, consider the tool’s performance in terms of query speed and data processing capabilities, especially when dealing with large datasets or complex calculations.
7. Consider Customization and White-Labeling: Your embedded BI solution should feel like a natural extension of your app, not a tacked-on feature. White-labeling capabilities allow you to customize everything from backgrounds and logos to visualization types, ensuring the BI tool seamlessly blends into your product. This level of customization not only enhances the user experience but also reinforces your brand’s identity within the application.
8. Evaluate Vendor Support and Community: Even the best embedded tools can run into issues. That’s where strong vendor support and an active user community come into play. Look for vendors that offer comprehensive support services, including training, documentation, and responsive customer service. An active user community can also be a valuable resource for troubleshooting and sharing best practices.
9. Test Before You Commit: Finally, don’t just take a tool’s marketing at face value. Test it in a real-world scenario. Many vendors offer free trials or pilot programs—use them. Gather feedback from your team, see how well it integrates with your existing systems, and evaluate whether it meets your needs in practice. This hands-on experience will give you confidence in your choice and help you avoid costly mistakes.
Traditional BI vs Embedded BI: 5 Key Differences
1. Workflow Integration
- Traditional BI: Requires users to leave their primary application and access a separate BI tool. This means interrupting your workflow to get the data you need, which can slow down decision-making and reduce efficiency.
- Embedded BI: Integrates directly into the applications you already use, keeping data insights within your workflow. This seamless access to analytics ensures that data-driven decisions happen in real-time, without breaking your stride.
2. User Experience
- Traditional BI: Often seen as complex and requiring specialized skills to navigate. Users need to learn a new interface and work outside their usual environment, which can lead to lower adoption rates, especially among non-technical users.
- Embedded BI: Designed to be user-friendly, with a focus on making analytics accessible to everyone, not just data experts. By embedding analytics into familiar tools, it simplifies the experience and encourages broader usage across the organization.
3. Contextual Relevance
- Traditional BI: Provides powerful analytics but often lacks context because it’s separate from the operational environment. Users must interpret data independently and apply insights back to their work.
- Embedded BI: Delivers insights within the context of the task at hand. By embedding analytics into your existing software, the data becomes directly relevant to your current operations, making it easier to apply insights immediately.
4. Adoption and Engagement
- Traditional BI: Adoption can be challenging because users have to invest time in learning a new tool, and the separation from their main applications can make regular use feel cumbersome.
- Embedded BI: Drives higher adoption by making analytics a natural part of the user’s daily tools. Increased engagement leads to better data-driven decisions across the board, as more users can access and understand the insights.
That being said, many modern embedded BI tools now offer a hybrid approach, combining both Embedded Analytics and traditional internal analytics. This dual capability allows businesses not only to deliver data more effectively to end-users but also empowers internal teams to maximize the value they extract from data, enhancing overall organizational intelligence.
Common Misconceptions About Embedded BI
Myth: Embedded BI is Difficult to Implement
Reality: There’s a misconception that implementing Embedded BI is a complex, time-consuming process. In reality, many modern Embedded BI solutions are designed with ease of integration in mind. BI vendors offer robust APIs, toolkits, and support that simplify the process, allowing for quick and efficient implementation without significant disruption to existing workflows.
Some even allow you to embed dashboards using just iframe or sharable links.
Myth: Embedded BI Requires Extensive Technical Expertise
Reality: While it’s true that some technical knowledge is needed, the belief that only IT professionals or data scientists can manage Embedded BI is outdated. Many solutions today are user-friendly, offering intuitive interfaces that empower non-technical users to self-serve report building, or interact with data and gain insights without needing deep technical expertise.
Myth: Embedded BI is Just a Fancy Add-On
Reality: Some see Embedded BI as a non-essential feature—nice to have, but not critical. In contrast, Embedded BI can be a game-changer for your users, providing real-time insights directly within the context of day-to-day operations.
This integration helps your users enhance productivity, drives better decision-making, and ultimately adds significant value to the competitive offering.
Myth: Embedded BI is Cost-Prohibitive
Reality: There’s a common belief that Embedded BI solutions are expensive and not worth the investment. However, with a variety of pricing models and scalable options available, businesses of all sizes can find cost-effective solutions that fit their budgets while still delivering powerful analytics capabilities.
Final Words
Measuring the success of Embedded BI goes beyond just counting the number of dashboards created or tracking how often reports are generated. The real metric of success lies in user adoption and engagement. Are your users regularly interacting with the embedded analytics? Are these interactions driving better decision-making and leading to tangible business improvements?
To truly gauge the impact of Embedded BI, you need to focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect its influence on users' engagement For instance, a noticeable increase in data-driven decisions or a significant reduction in the time it takes to gain insights are strong indicators that your Embedded BI implementation is on the right track. These metrics not only highlight the effectiveness of the tool but also demonstrate how deeply it’s integrated into the decision-making fabric of your business.
What's happening in the BI world?
Join 30k+ people to get insights from BI practitioners around the globe. In your inbox. Every week. Learn more
No spam, ever. We respect your email privacy. Unsubscribe anytime.

